Baccharis pilularis
coyote bush
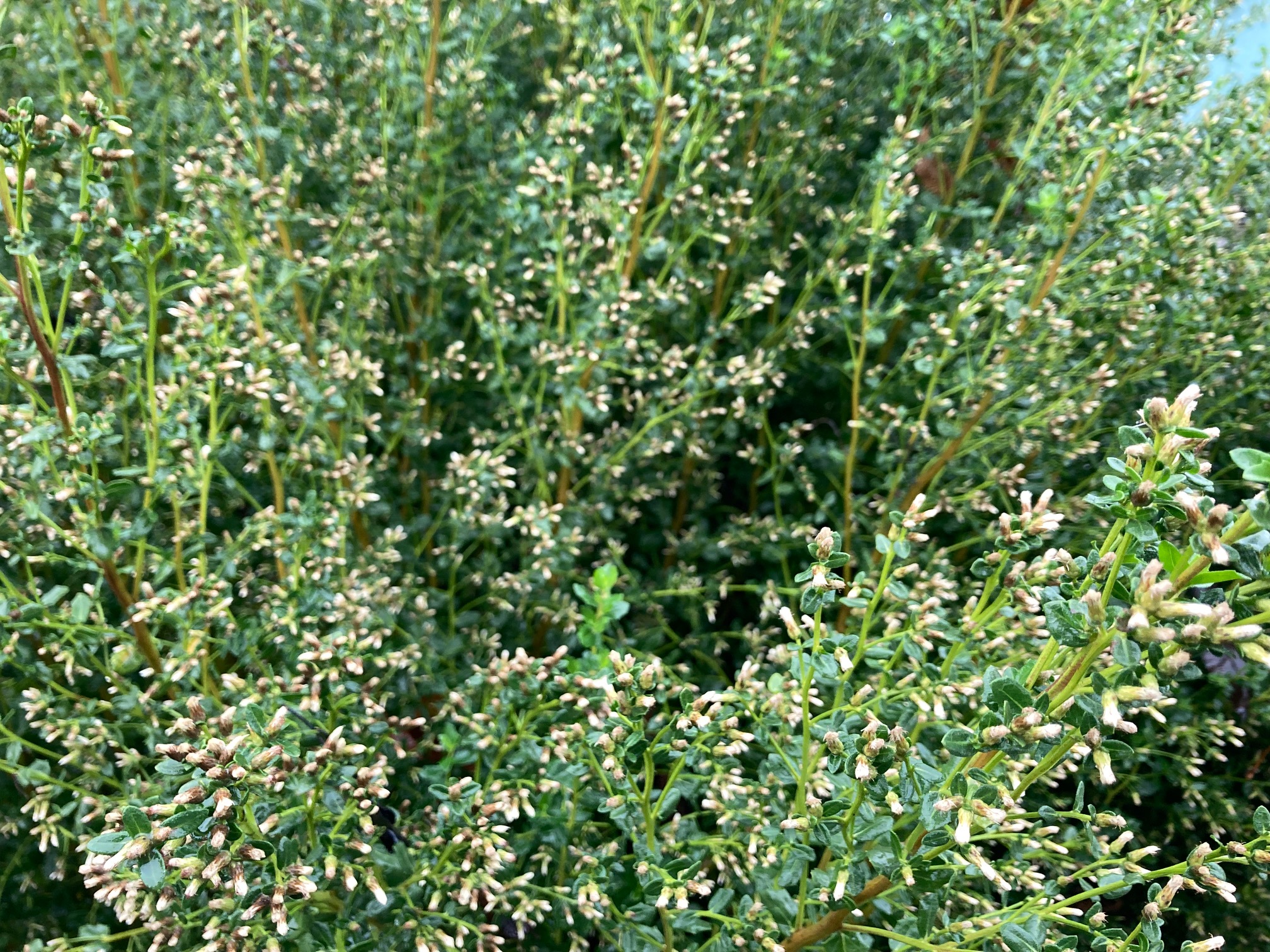
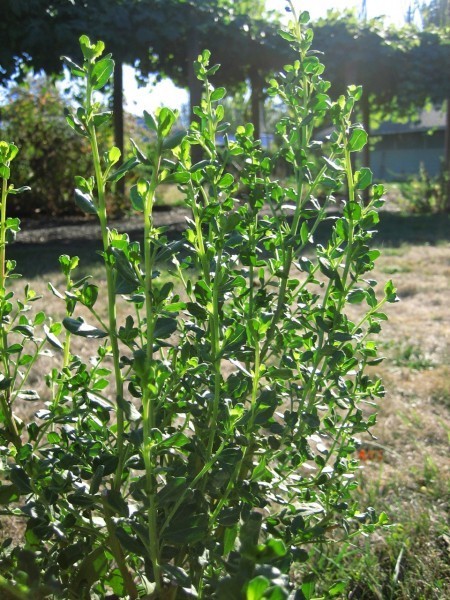
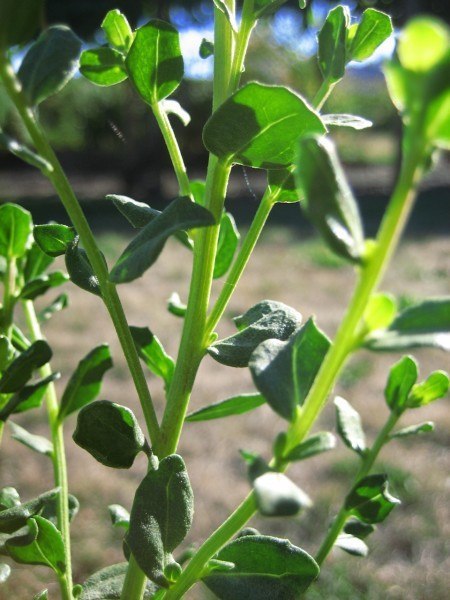
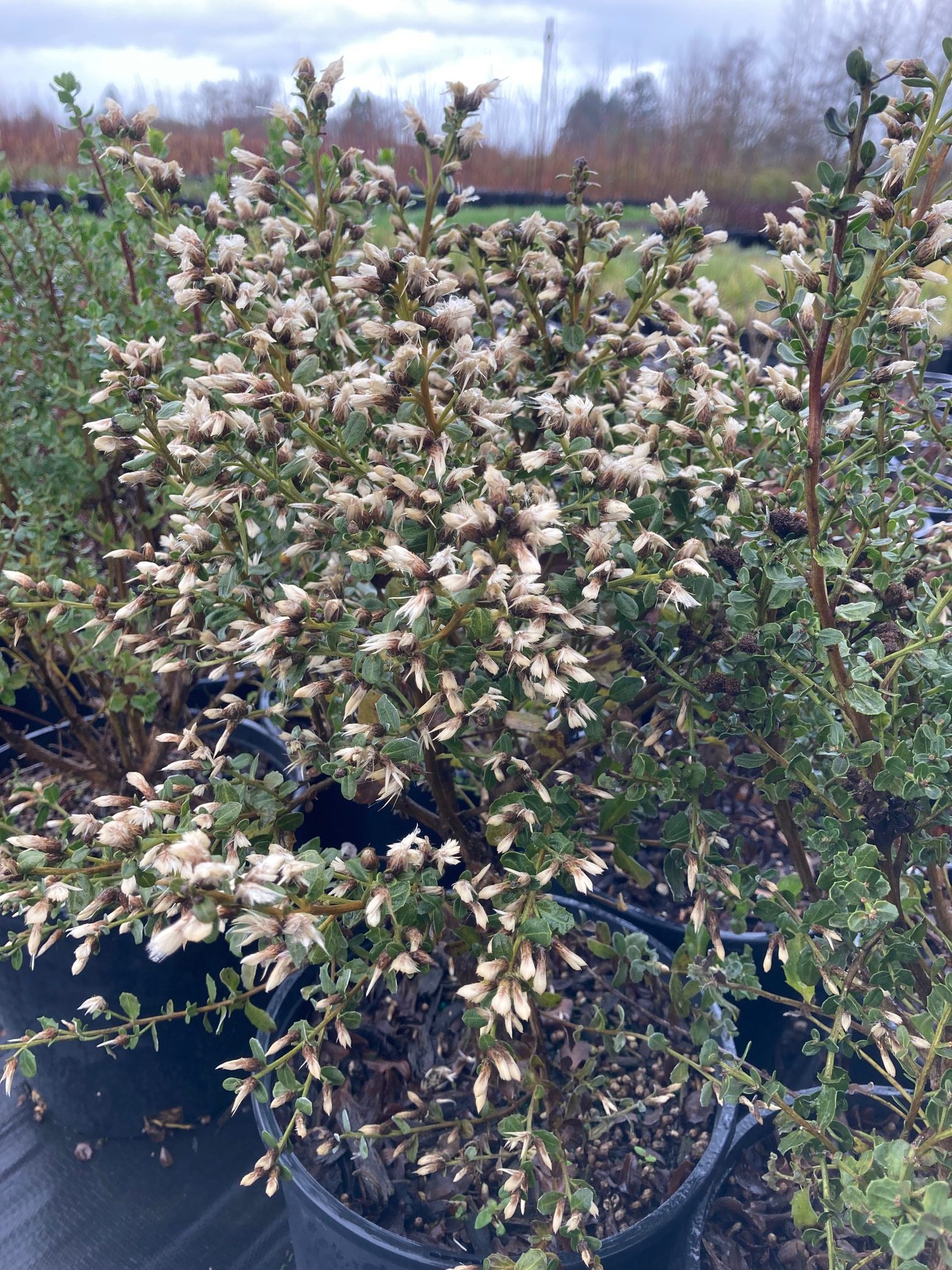
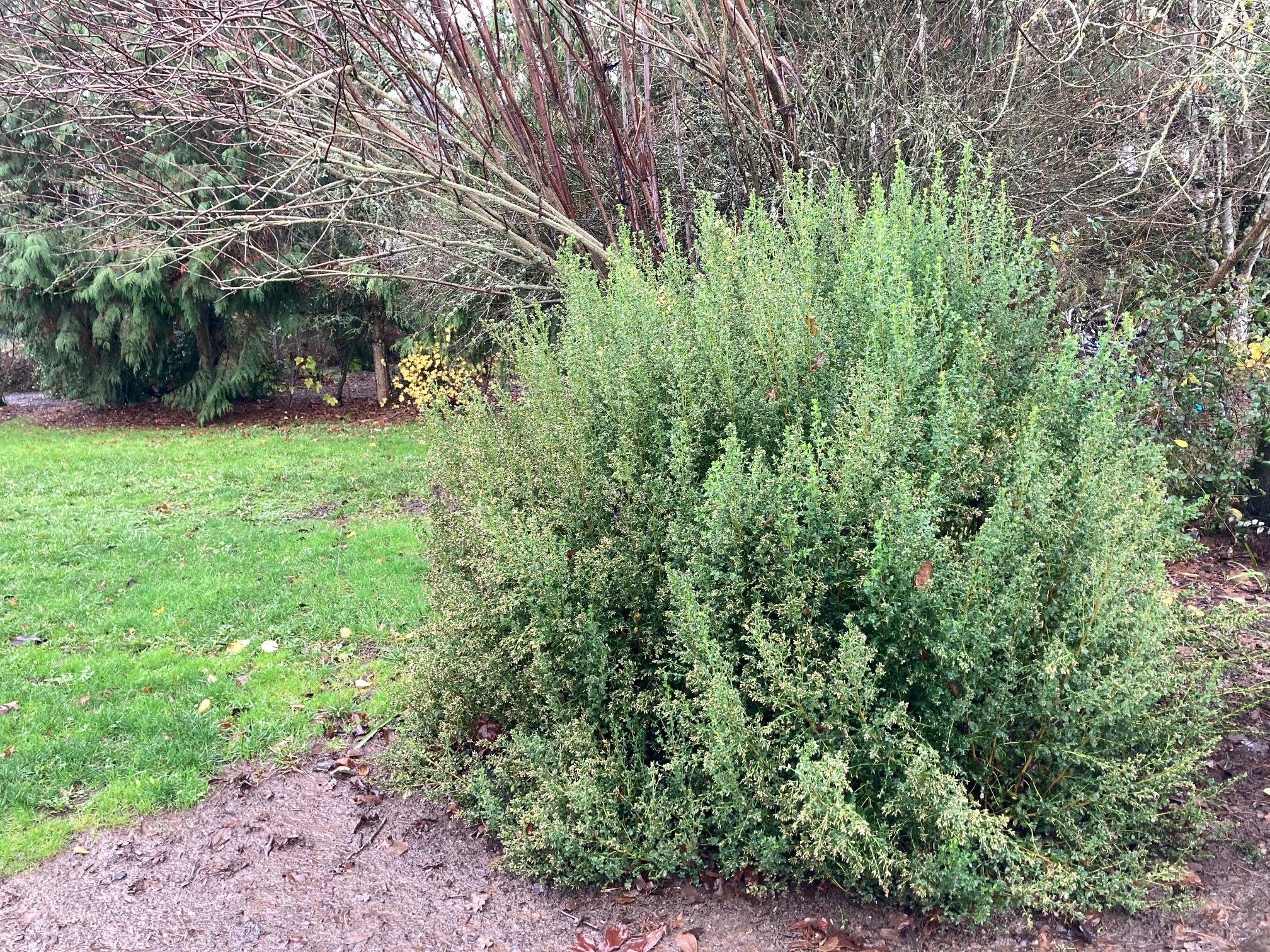
Habit: growing in two different forms, the coastal version of Baccharis pilularis is low and prostrate, while the interior form is upright and shrubby. The evergreen leaves are covered with resin glands, which vary the coloring of the shrub from dark green to gray. The flowers are dioecious, meaning the female and male flowers are on separate plants. As part of the Asteraceae family the inflorescences are composed of many disc flowers. It has an extensive root system with the tap root growing up to 10 ft long, as well as forming many outward-growing roots.
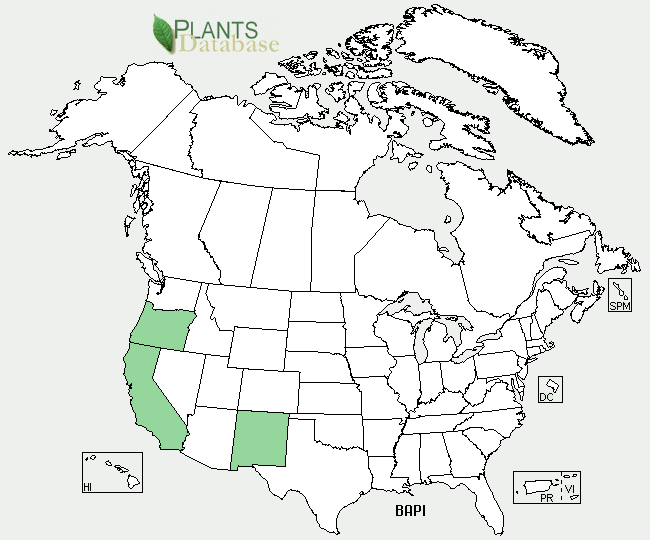
Ecology: found in Oregon, California and New Mexico, coyote bush prefers settling near the coast, or in canyons from sea level to 2000 ft (600 ft).
Growing Conditions: full sun, Baccharis pilularis can tolerate drought once established, and is more deer resistant than most plants. When planting, plant further apart than normal as the underground growth is much greater than that above ground.
In the garden, coyote bush can be used as a hedge, or in areas that are prone to erosion. It should be pruned back periodically simulating fires/grazing that would occur naturally in the wild. Coyote bush is beneficial as habitat for birds, and other small animals; cover for native perennials to establish themselves; nectar for many insects.
Specs
Evergreen Shrub
1-9 ft. (0.3-3 m)
2-9 ft. (0.6-3 m)
5-11